SEO optimization of a website in search engines is very important for most businesses that offer products or services on the internet.
SEO is an effective way to rank high in search results and get a consistent number of visitors for a long time.
Here in this blog post, we will discuss what is SEO, how it works, and the main types of SEO optimization.

Table of Contents
What Is SEO?
What is SEO – The SEO acronym stands for Search Engine Optimization. In simple words, SEO is a methodology, it’s a set of actions we do internally and externally to optimize the website for increasing the ranking in search engines.
Simply said, high-quality SEO helps the site to climb in search engine results, and traffic will be higher if that page ranks higher in search results.
Therefore, we can say that search engine optimization is one of the most effective techniques for attracting consistent traffic to the website for a long period of time.

How Does The SEO Work?
The principle of SEO optimization looks very simple: the user enters a query of interest to him in a search engine, and the search engine pulls a list of websites that contains resources in a certain order.
After that, the potential client gets acquainted with a brief description of the resource and clicks on it if it interests him. The higher ranking in the search results gets more traffic since the user usually does not go beyond the first page of the search results.
The principle of displaying search results on demand uses a complex sorting formula that takes into account dozens of parameters. At the same time, the exact algorithm for such a ranking is not disclosed by the owners of Google or any search engine company, who shares only the general principles of building a high-quality and useful resource for people, helping to climb to the top of the search engines.
In practice, without the use of SEO optimization techniques, it is almost impossible to bring a site to the first page of search results in highly competitive commercial topics, even if its content and technical implementation are perfect.
High-quality SEO is not just building links or creating useful content. It requires a lot of strategic work to get higher rankings in search engines.
Who Uses The SEO?
SEO is suitable for everyone who is going to or is already selling products or services on the internet, looking for clients, customers, partners, etc. It makes sense to promote the site if:
- If your product is in demand among a wide range of audiences;
- Does your company have online competitors?
- The legal products are allowed for sale at the government level;
- Are you willing to wait at least a few months for results?
- If you are looking for relatively inexpensive website promotion systems that are effective and reliable in constantly attracting traffic;
- If you are ready to invest time and finances in your site, constantly develop and improve it;
- If you plan to stay in the market within your niche or expand over time.
To achieve quick results, SEO optimization is not suitable. It is designed for long-lasting results. You will be able to see the first results at least after 2-3 months of the start of work not earlier than that. Of course, it varies depending on the industry, competition, and other factors.

What Does The SEO Optimization Mean?
SEO-optimization involves the implementation of a number of actions aimed at gaining credibility with the target audience of the search engine.
Determining the criteria that have the greatest impact on the ranking of the site in the SERP, and purposeful work with the resource parameters that improve them.
Formation of a relevant thematic core, the grouping of words by subject, and redistribution of the site structure. Internal and external search engine optimization of the resource.
Studying the usability of the site and the behavioral factor, which plays an increasingly important role in evaluating the quality of the resource by search engines.
Constant collection and analysis of statistics of visitors to the site from the search engine and their actions directly on the resource.
Adjustment of the promotion strategy based on the analysis of the collected statistics and its dynamics.
Naturally, each subtask is divided into many points during work, which can be performed by different specialists.
How To Start SEO Optimization?
First of all, determine the purpose of SEO optimization and how its effectiveness will be measured. For example, SEO optimization may have the following goals:
- Bringing the site to the top of certain search queries;
- Increase in website traffic;
- Increase in conversions;
- Improving the position of the site in the search in relation to the projects of competitors, etc.
Also, if you are going to engage in SEO-optimization of the site, you should determine those categories and web pages that are the most relevant and important. Make an action plan with a list of all the necessary work and indicate their priority:
- The order of optimization of the site pages;
- The procedure for adding content to the site;
- Resources where you can place links to your project, etc.
Why Do You Need SEO Optimization?
SEO optimization is aimed at improving the position of the site in SERP for selected search queries, the purpose of SEO is to increase traffic, increase the visibility, the popularity of the website, increase the number of leads and sales.
Without SEO optimization, your website will be ignored among the hundreds and thousands of other websites for the same topic that is present on the web. No ranking means users will never be able to find it using search engines.
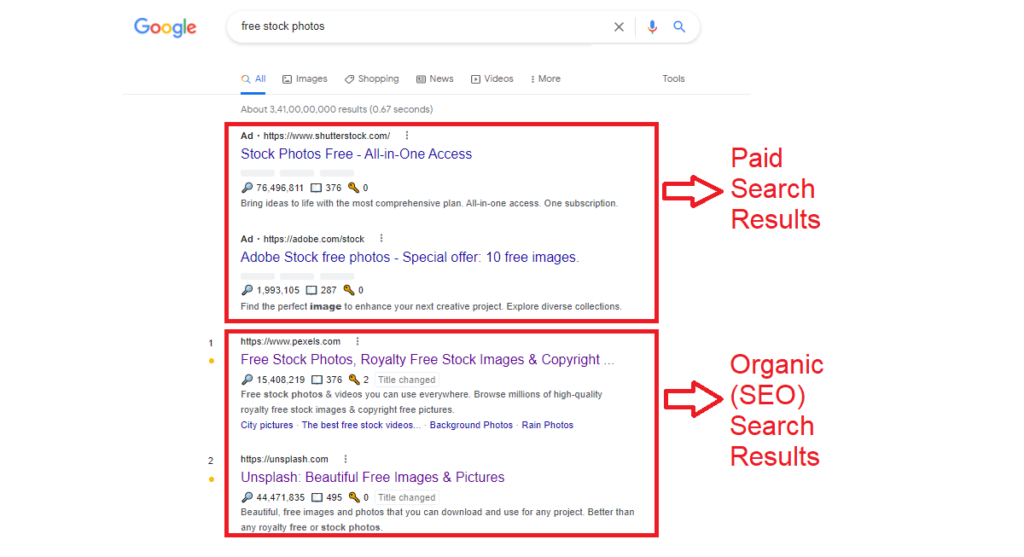
The higher the position of the site, the more visitors you will receive. Part of the traffic will be taken by contextual paid advertising, but most users choose sites from the top of organic search results.
Therefore, it is very important to regularly work on improving the position of the site and not stop when you reach the top, otherwise, you may be forced out by competitors.
Why SEO Optimization Is Beneficial?
Investing in SEO promotion is a more profitable type of investment than using paid search advertising since paid search requires regular replenishment of the budget for significant amounts. When using SEO after entering the TOP, you can reduce the cost of promotion by doing only regular creation of new high-quality content.
Search engine optimization has benefits such as:
- Low cost to attract the client;
- The lasting effect even after completion of promotional work;
- Greater trust from clients, who may feel that lower-quality projects need context than those that have taken first positions naturally;
- Reaching a large audience, etc.
Why Should You Pay Attention To SEO?
Billions of people search the internet every day. Organic traffic is extremely powerful, not only because it is large in terms of quantity, but also because it consists of specific requests, often containing certain content.
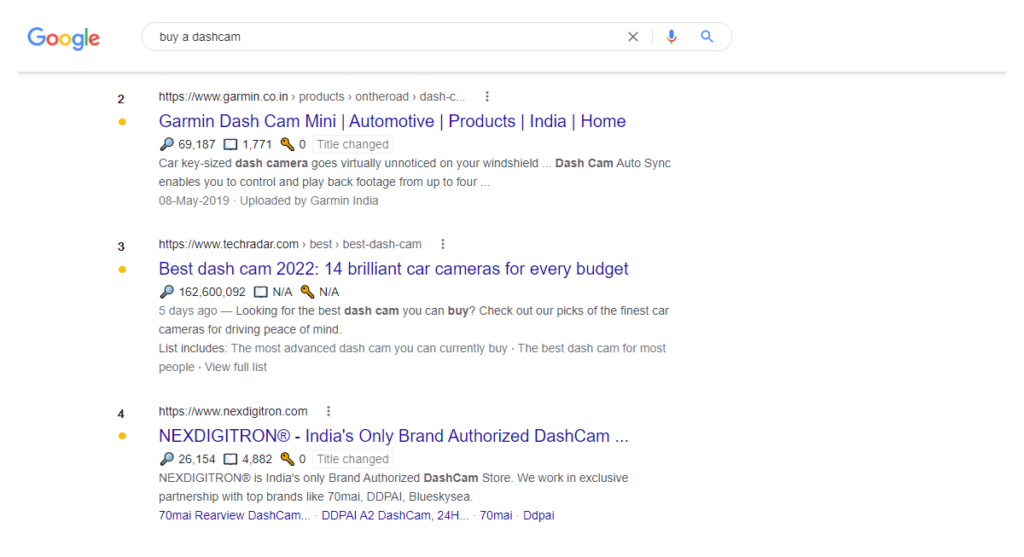
Let’s imagine a situation. For example, you sell video recorders. Would you prefer to advertise your product on a billboard in a certain area of the city so that every car owner in that area sees this advertisement (regardless of whether they need a DVR or not)? Or offer a product every time someone types the query: “buy a dashcam” in the search bar?
Most likely the second option, because these users have a commercial intent in their request. That is, they literally stand up and say they want to buy what you offer.
What Really Helps To Increase Traffic From Search Engines?
Search engine algorithms are constantly updated, and every year it becomes more and more difficult to get to the top of the results and keep your positions there. And many cheap and easy ways to improve your rankings have become extremely risky and face penalties from search engines.
So what works? How do Google, Bing, and other search engines determine which pages to return in response to what people are looking for? How do you get all that valuable traffic to your website?
Google’s algorithm is extremely complex, and here are the basic principles it uses to rank websites:
Google searches for pages that contain quality and relevant information about the user’s query.
It determines relevancy by “scanning” your site’s content and evaluating (using algorithms) whether that content matches what the user is looking for, typically based on the keywords contained in the content.
Google defines the “quality” of a site in many different ways, but what is still important to it is the quantity and quality of other websites that link to your page and to your site as a whole.
The Google algorithm also evaluates additional elements to determine where your site will rank, such as:
How do people interact with your site (do they find the information they need and stay on the site, or do they return to the search page and follow another link? Or do they just ignore you in the search results?)
Your website loading speed and mobile-friendliness
How much unique content do you have (vs. low-value content or duplicate content)
The Google algorithm considers hundreds of ranking factors in response to search queries, and they are constantly updating and improving their process.
Stages Of Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Niche, Keyword Research For SEO
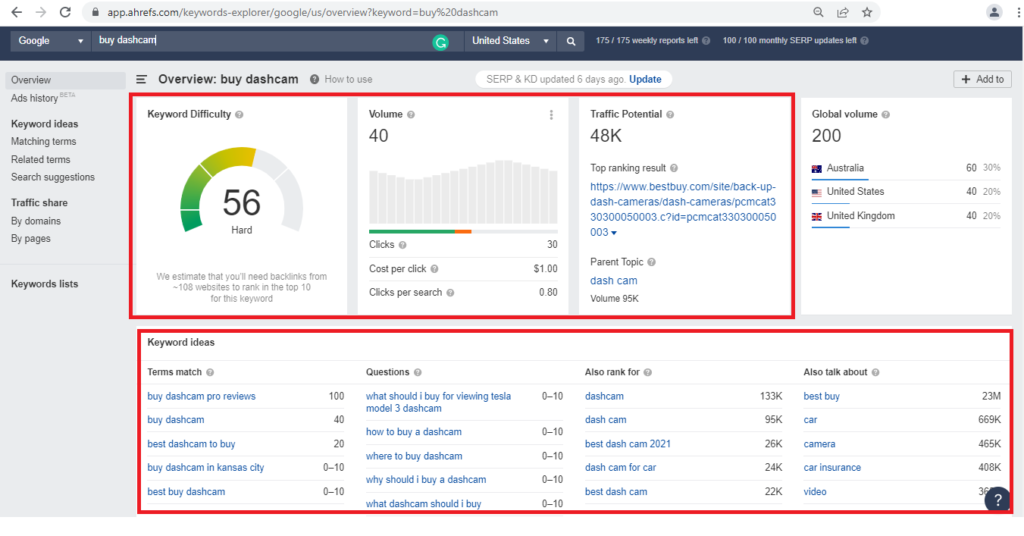
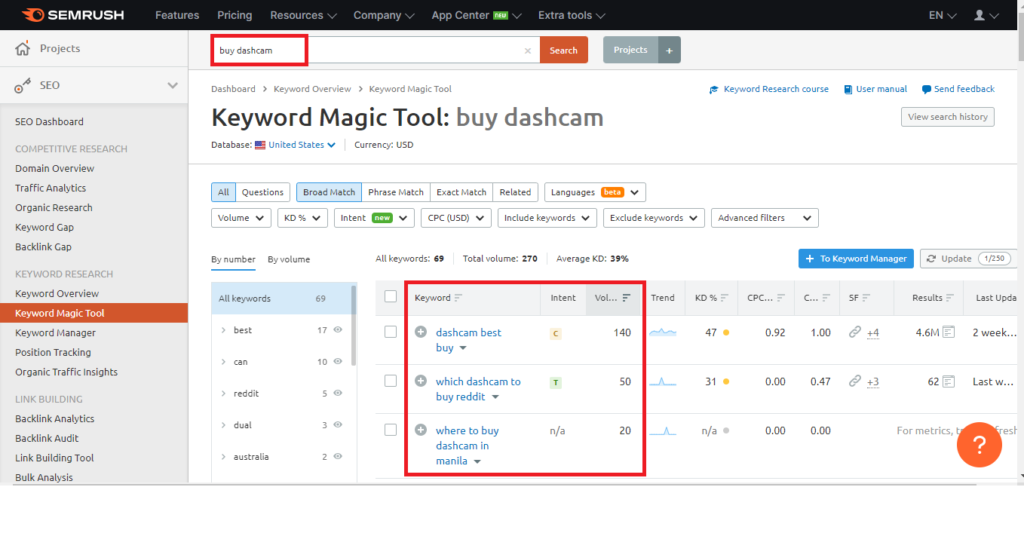
The first step in search engine optimization is to correctly identify what you are actually optimizing for. This means identifying the queries people are searching for or the keywords you want your site to rank for in search engines.
Sounds simple enough, right? I want my company to show up in searches when people search for “DVRs” and maybe when they type “buy dashcam”.
But in fact, not everything is as simple as it seems. There are a few key factors to consider when determining the keywords for which you want to promote your site:
Search volume: The first factor to consider is the number of people (if any) who are searching for a given keyword. The more people who search for a keyword, the wider the audience you want to reach. Conversely, if no one searches for a key, then there is no audience that could find your content using the search.
Relevance: If a product or service is frequently searched for, that’s great. But what if that query isn’t entirely relevant to your potential customers?
Relevance seems obvious at first: if you’re selling enterprise email marketing automation software, you don’t want to show up for search terms that have nothing to do with your business, like “pet products.”
But besides this, you should take into account for which companies you sell your product, in which territory, and other equally important factors.
Competition: In SEO, too, you must consider the potential costs and likelihood of success. For SEO, this means understanding the relative competition (and the likelihood of ranking) for specific terms.
First, you need to understand who your potential customers are and what they are most likely to be looking for. If you don’t yet understand who your audience is, think about it.
This is a good start not only for SEO but for business in general.
To better understand your audience, ask a few questions:
- What interests them?
- What are their problems?
- What language do they use to describe needs, enter a request?
Who else do they buy things or services from? (These may be your competitors. But, in addition, the answer to this question may provide indirect clues in determining your target audience).
Once you’ve answered these questions, you’ll have an initial “basic list” of possible keywords and domains. This list will help you get more keywords, search volume, and competition metrics.
Take a list of the main terms your prospects and clients use to describe what you do and start typing them into your keyword tools.
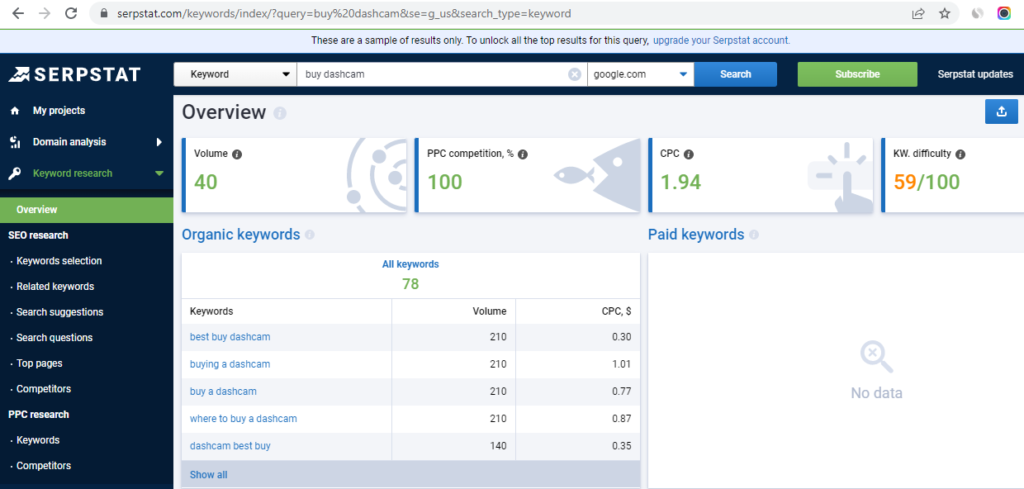
You can use various keyword suggestion tools, but the basic idea is that at the initial stage, you will need to try to collect the maximum number of the most relevant keywords and expressions.
If you already have an active website, then chances are you are already getting some traffic from search engines. The Google Search Console Tool can also give hints when working with requests:
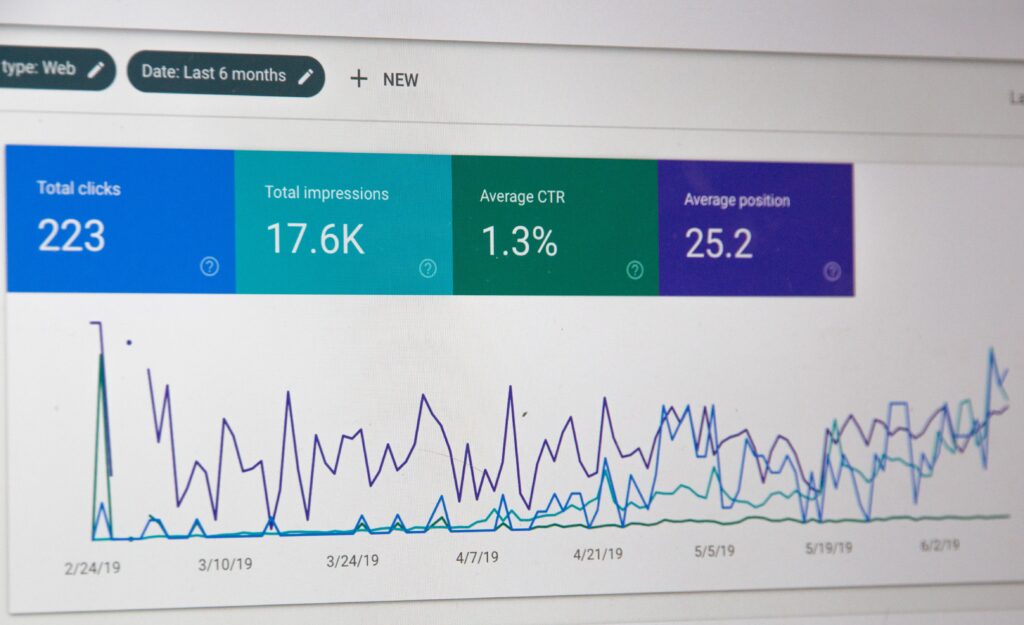
After you understand who your potential customers are, what they are looking for and how they enter a request; Having analyzed the keywords that bring traffic to competitors and studied the queries that attract traffic, you need to determine by what criteria your site can rank and where to focus your SEO efforts.
SEO On-Page Optimization
Once you have a list of keywords, the next step is to embed targeted keywords into your site’s content. Each page should be focused on the main query or group of queries.
Let’s look at a few important basic page elements that are essential if you want to drive targeted traffic to your site:
Meta Title
This tag helps search engines understand the actual meaning of the page, what it is about, and also recognizes the queries you want to rank for. And this is the most effective place to place your keywords.
But do not forget that Google and other search engines still punish aggressive and manipulative use of keywords.
The Title tag is not the main title of your page. The title you see on the page is usually an H1 or H2, HTML element.
The Title tag is what you see at the very top of the browser, and it’s populated with the page’s source code in the meta tag:
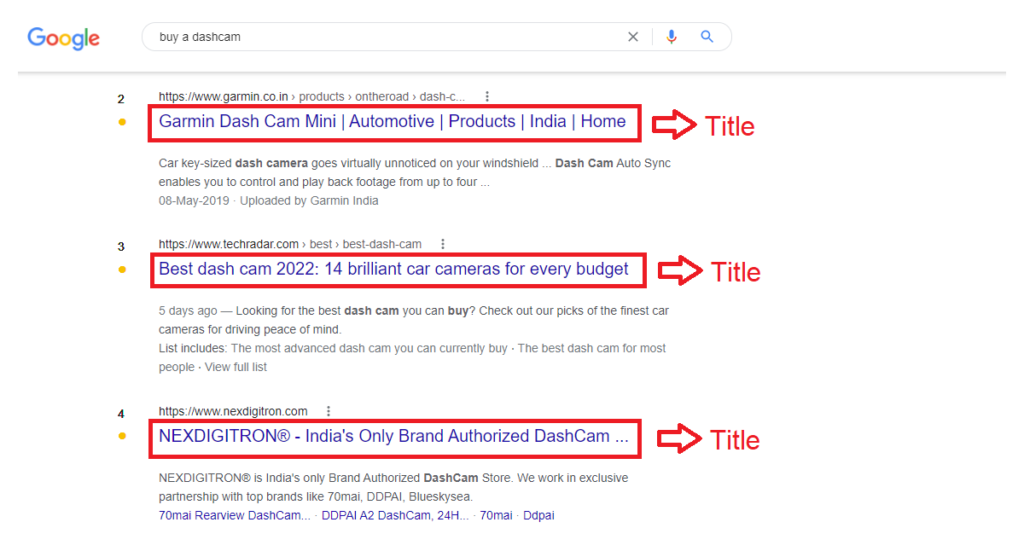
The length of the title that is shown on Google will vary (it’s based on pixels, not character count), but 55-60 characters on average are the ideal size in practice.
When composing the Title, remember that this is what the user sees in the search results, what gets into the snippet using the snippet optimizer tool.
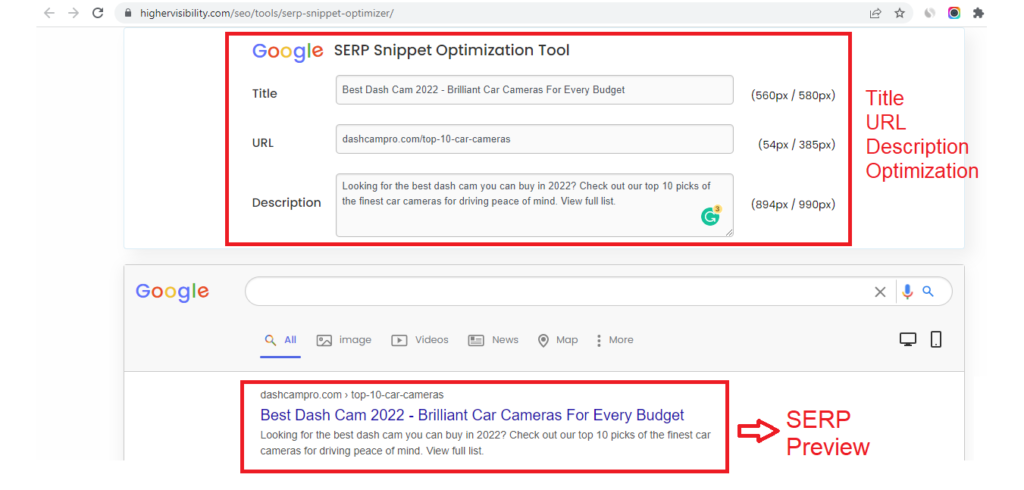
The title should give an answer to the user’s main intent, not break off in half a word and be written in human language, and not “Buy DVR Moscow”.
Meta Description
While the title tag is actually your site’s title in the SERPs, the Description (another HTML meta element that can be updated in the site’s code but not appear on the page) is actually additional advertising for the site.
Google takes some liberties with what to display in a snippet, so your meta description may not always appear. Instead, Google’s crawler can rip out the piece of content that it thinks best matches the description of the page.
But if you can write a compelling page description that convinces people to click on the link, you can significantly increase traffic to your site. (Remember: appearing in search results is only the first step! You still need search engines to come to your site.)
Example Description in Google search engine:
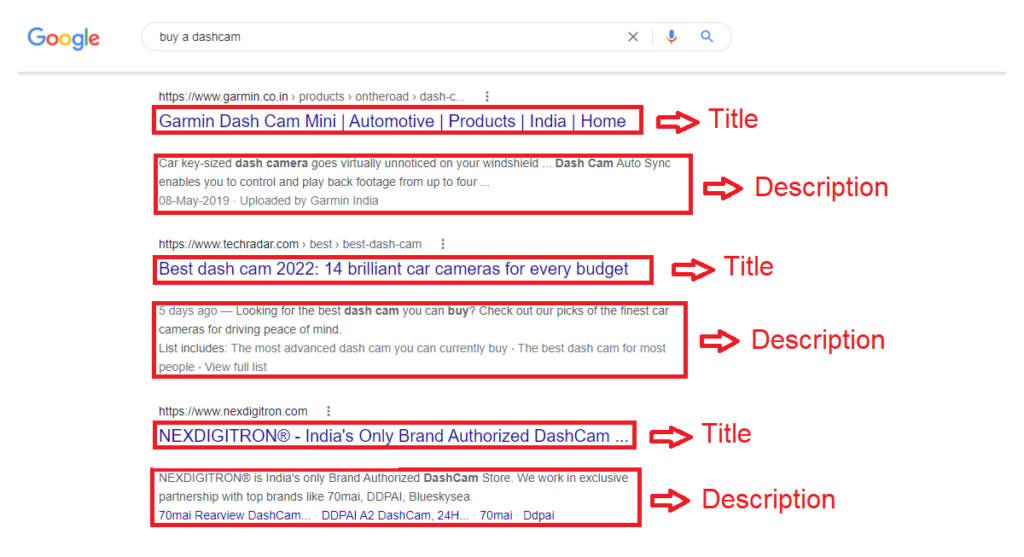
Body – Page content
Of course, in addition to the meta description (Title and Description), the actual content of the page itself is also important. Different pages serve different purposes.
Google and other search engines are increasingly favoring certain types of content, and there are a few things to keep in mind when creating any of the pages on your site:
Extensive And Unique Content
There is no magic number in terms of word count, and if you have multiple pages of content on your site with a few hundred words, you won’t lose favor with the search engines. But more often, longer unique content is preferred.
If you have a large number of very short (50-200 words) pages or a lot of duplicate content where nothing changes except for the title tag of the page, this can negatively affect the position of the site.
Look At Your Site’s Overall Content
Is a large percentage of your pages skinny, duplicated, and of little or no value? If yes, try to find a way to “make” these pages better, full of content.
Check your analytics to see how much traffic these pages are getting, and simply exclude them (using the noindex meta tag) from search results so that search engines don’t think you’re trying to flood their index with lots of low-value pages in an attempt to rank them up.
A tool for webmasters will help you find low-value and low-quality pages on the site.
User Experience & User Engagement
Search engines, especially Google, are paying more and more attention to engagement and user experience metrics.
You can positively influence these indicators by making sure that your content responds to the user’s request, it (the content) is really useful, interesting, and can be interacted with.
Make sure the pages load quickly and don’t contain unnecessary design elements or, for example, overly aggressive ads above the content.
“Sharability” or “sharing ability”: The ability to share this specific content on social networks.
Image Alt & Title Attributes
How you mark up your images can affect not only how search engines perceive your page, but also the amount of search traffic generated by image searches on your site.
The alt attribute is an HTML element that allows you to provide alternative information for an image if the user cannot view it.
Your images can break over time (files get deleted, users can’t connect to the site, etc.), so a useful image title and alt description can be important in terms of overall usability.
It also gives you another opportunity – beyond the content – to help search engines understand what the page is about.
It is not necessary to “stuff” with Alt keywords. Just don’t skip it and try to give a complete and accurate description of the image (imagine describing it to someone who can’t see it – that’s what the Alt attribute is really for!).
URL Structure
The structure of your site’s URL can be important both in terms of tracking (you can more easily segment data in reports using a segmented logical URL structure) and in terms of being able to share the URL of the page (shorter descriptive URLs are easier to copy and paste and tend to be erroneously cropped less often).
Once again: don’t try to cram in as many keywords as possible; create a short, descriptive URL.
What’s more: if you don’t have to, don’t change your URLs. Even if your URLs aren’t “beautiful”, if you don’t see them negatively impacting users and businesses in general, don’t change them to be more keyword-focused for “better SEO”.
If you really need to change the URL structure, make sure you are using the correct 301-page redirect. This is a common mistake that companies make when changing the design of their sites.
Schema.org Markup
Finally, once the basic page elements are complete, you can go further and help search engines understand your site’s pages. The schema.org markup makes the SERP snippet more organized and attractive to users:
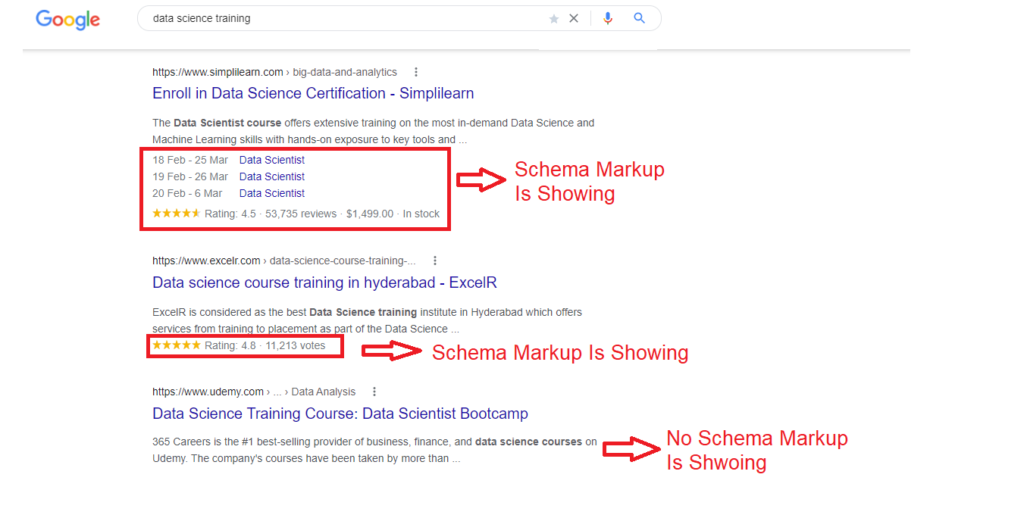
The markup doesn’t make your page rank higher in search results (it’s not currently a ranking factor), but it does give you some edge over competitor sites that don’t use schema.org.
There are many different types of markup that you can include on your site. For example, to correctly display a link on social networks, use Open Graph markup.
Information Architecture And Internal Links
Information architecture describes how you organize pages. Building a site and linking between pages can affect the ranking of various content on your site.
The reason for this is that search engines generally treat links as a “vote of trust” and a means to help understand what a page is about and how important it is (as well as how much it should be trusted).
Search engines also take into account the text you use for a link. This text is called anchor text – using descriptive text for the link helps Google understand what this page is about.
But do not forget that too aggressive use of keywords in anchor texts threatens the site with sanctions.
A link from a major media outlet is an indicator that your site may be important to search engines and users, and if you repeatedly actively link to a particular page from your site, then this is an indicator to search engines that this particular page is very important to the site.
In addition, we can say that the pages that get the most links from external resources have the most power to help other pages on your site rank in the search results.
This principle refers to a concept called “PageRank”. Let’s look at a short example. It will help you understand the concept of how to link ratio (or the number and quality of links linking to a page) affects the architecture of a site and how you design linking.
Let’s imagine that we have a site offering snow removal services:
We publish an interesting study on the effect of snow on construction in winter in cold climates. It is referenced from all over the internet.
The study is published on the main page of the site. All other pages are simple, sales-oriented pages explaining various aspects of the snow removal company’s offerings. No external site is linked to any of these pages.
The study itself can rank well in search results for various phrases. Sales-oriented pages are much smaller.
However, by linking from our research to the most important sales-oriented pages, we can pass on some of the weight of linking to research sites to them.
These pages, of course, will not be as well-positioned to rank in the search results as our study, but they will be in a much better position than when they did not have any authoritative sources (on our or other sites) pointing to them.
It is very important to have strategic links to the most important pages of your site from your home page.
Information architecture can be an extremely complex topic, especially for large sites, but the most important things to keep in mind are the following:
Try to understand which pages are most often linked to (you can use tools such as Ahrefs, Serpstat, or view reports on the most popular pages in Google).
Keep the most important pages (which you use to target your most valuable keywords) “high” in the site architecture.
This means that you will often link to them in navigation elements and, if possible, from the pages that are most often linked to.
In general, if you want a large and effective site information architecture, you need to link as much as possible from the home page and the most mentioned ones to the ones you want to “pump”.
Content Marketing And Link Building
Since search engines still factor in the influence of a site’s backlinks in the ranking (especially Google’s algorithm is heavily based on links), having a number of quality links to your site are important to drive search traffic.
You can do the best work on internal SEO, but if other resources do not link to your site, then the chances of appearing on the first page of search results are extremely small.
There are several ways to get links to your site. But as every year Google and other search engines become more and more sophisticated, many of these methods become risky (even if they are still effective in the short term).
If you are new to SEO, then risky and aggressive ways to get links are not your option. You will not know how to correctly assess risks and avoid “traps”.
Also, trying to build links specifically to increase search engine rankings will not provide any business value. And in the event of a change/update of search engine algorithms, the site can drastically sink in positions.
A more appropriate way to build links is to focus on general marketing approaches such as creating and promoting useful content that also includes the specific queries you want to rank for.
The process of creating and promoting content that will contain links and shares on social networks is labor-intensive. There are many different ways to create content effectively and rank well in search results.
However, most approaches will require you to do variations on the following three basic steps anyway:
* Identify and study the audience that will link to you
If you can be of service to content creators in your niche, you will begin to build powerful relationships that will pay dividends.
Before you create the bulk of the content, you should think about how it will be shared: who will be sharing and why?
* Determine what content you can create and how you will promote it
At this stage, you should understand what content will be useful to your target audience, and what kind of content other people will want to share.
There are several different types of such content:
- Create something that can solve the problems of your potential customers.
- Use what already works. Learn information in your niche from competitors and create something two or three times better.
- This way you can reduce risk and make your content as resilient as possible.
- Benefit from expert opinion. Talk about something you use every day, get feedback from interested people in your niche, and share that content (positioning those people as experts).
- When you mention someone or talk about someone’s product, it’s likely that the content will be shared and promoted.
* Use Keywords
And, of course, don’t forget to use keywords in your content.
This does not mean that you need to insert keywords wherever you need to when you create some content.
This means you can use keywords and phrases as a means of discovering your target audience’s pain points (if people turn to search engines when they’re looking for something, they need an answer to a question they’re having!).
Useful Read: Content Marketing Guide
Technical SEO Audit: General Techniques
Recently, link building and creating quality content have become the most important aspects of website promotion in search networks.
But still, don’t forget about the so-called “traditional SEO”, it is still fundamentally important for generating traffic to your site.
Technical SEO for larger, more complex sites is actually a different story. But still, there are some common mistakes and issues that most websites face.
This information will be useful for any online business:
* Page Speed
Search engines have been focusing more on fast-loading sites for a long time now – the good news is that it’s not only good for search engines, it’s also good for your users and your site’s conversion rates.
Google has a helpful tool that gives you some specific suggestions on what to change on your site to improve its loading speed. Check your page speed insights here.
* Mobile Friendly
If your site is (or is likely to be) attracting significant search engine traffic from mobile devices, then how responsive it is will affect your rankings.
In 2021, mobile traffic is already exceeding desktop traffic in many niches.
First, Google, followed by other search engines launched algorithms that take into account the adaptability of the site for mobile devices when ranking. Such sites received the highest positions in mobile SERPs.
So, perhaps, today it is one of the decisive factors in ranking sites and should not be neglected.
You can test your site for adaptability in a simple and free Google’s mobile-friendliness testing tool.
* Server Response Code
Server response codes are an important technical feature of SEO. If you are not very tech-savvy, then this might be a tricky topic for you.
However, you still need to make sure that working pages return the correct code (200), and that pages that are not found also return a code and indicate that they are no more (404).
An erroneous entry of these codes can indicate to Google and other search engines, for example, that a page with the answer “Page not found” is actually a valid page.
Such an error can negatively affect the ranking of the site and, in general, it’s indexing by search engines. In this case, use the tools for checking the server response.
* 301 Redirects
Improper implementation of redirects on your site can seriously impact search results.
If you want to move website content from one URL to another, you must remember that there is a 301 redirect (or permanent) and a 302 redirect (temporary).
Don’t use a 301 redirect unless you have a really good reason to do so.
* Duplicate Content
“Skinny” and duplicate content is another area that search bots pay attention to. By duplicating content (posting the same or nearly identical content on multiple pages), you reduce the number of links between two pages instead of concentrating them on one page.
Having a lot of duplicate content makes your site look “cluttered”, low-quality (and possibly manipulative) content in the eyes of search engines.
Duplicate content can be difficult to diagnose, but you can look at duplicate content pages in Webmaster Tools.
* Sitemap.xml
Sitemap.xml helps Google and other search engine robots (and other search engines) better understand the structure of your site and correctly find its content.
Just make sure you don’t include useless pages, and be aware that submitting a page to a search engine via a sitemap does not guarantee that the page will actually rank.
The sitemap only helps to see this page. There are many free tools for creating XML Sitemaps. In addition, in many cms of the site, you can create a sitemap yourself.
* Robots.txt, Meta NoIndex, and Meta NoFollow
Finally, you can tell search engines how you want them to treat certain content on your site (for example, if you don’t want them to crawl a specific section of your site) in your robots.txt file.
This file is usually created for the site at the initial stage of promotion, and, most likely, it is already on your site at yoursite.ru/robots.txt.
You need to make sure that this file does not currently block the necessary pages of the site, and also closes unnecessary or junk pages from indexing.
You can use the meta noindex and meta nofollow tags for similar purposes, although each function differently.
How to Track and Measure SEO Results
So, after creating useful and interesting content on your site and implementing all the steps above (and maybe more), how do you plan to track how well the site is performing?
At first glance, this question has a fairly simple answer – track by key indicators that you need to focus on. However, for each metric, there are several important factors to consider when measuring your site’s SEO performance.
* Keyword Rankings
Positioning your site against a list of keywords is, of course, not the final destination. You can’t pay your employees to rank. In addition, search personalization has made it even more difficult to track results.
But a rough idea of where your site ranks for top queries can be a useful indicator of the site’s health. High positions for a range of keywords are a good indicator of a site’s visibility in organic search.
This does not mean that you need to get too hung up on positions for any one query. Remember, your ultimate goal is to drive more relevant traffic that will drive the growth of your business as a whole.
If you’re selling dash cams, what’s more, important to you: ranking high for “buy a dashcam” or figuring out and implementing an SEO strategy that will help you sell more dash cams in the most cost-effective way?
Various tools, both paid and free, can help you monitor the position of the site. Most of them are similar in functionality, but also don’t forget about position monitoring in local or mobile search results.
If you’re a small business or just getting started with SEO, we’d recommend picking a free and easy-to-use tool and just keeping track of a few keywords you want to track to gauge your progress.
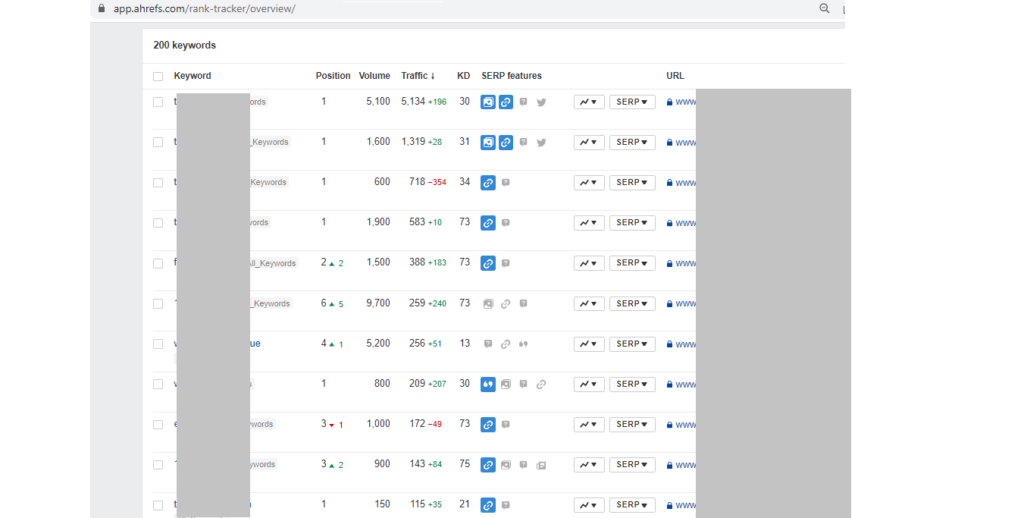
* Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the best indicator of your search engine optimization efforts. By analyzing organic traffic to a site, you can estimate the actual volume of visitors coming to your site and where they are going.
You can easily measure your organic traffic with most analytics tools – they are free and the most commonly used.
For example, on the main page of Google Search Console, you will immediately find statistics on traffic sources:
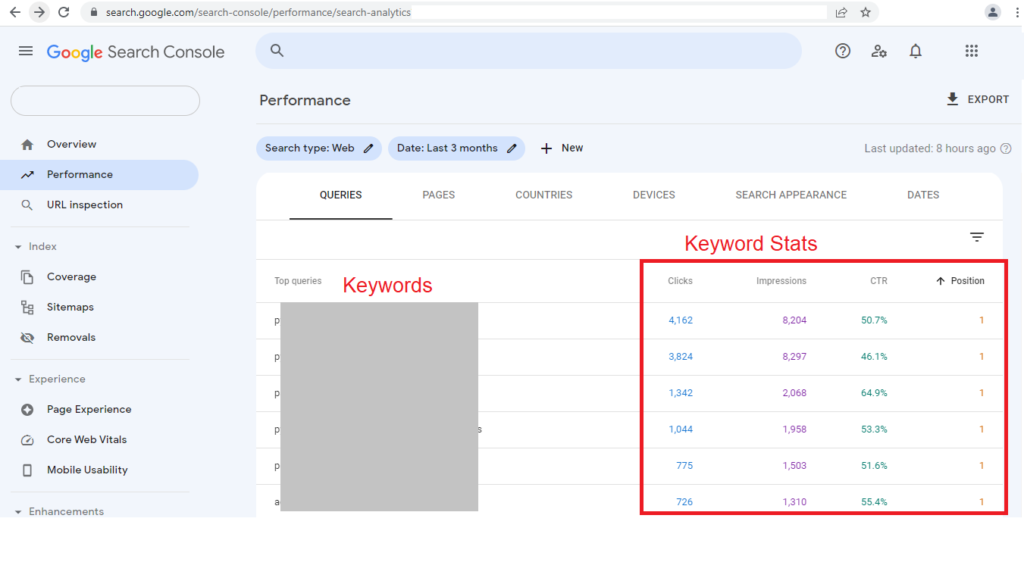
* Leads And Sales From Organic Search
Obviously, the main way to measure search engine optimization results should be actual leads, sales, revenue, and profits.
As with any other marketing tool, you need to understand: how does this activity help increase your profits?
The easiest way is to set goals or track eCommerce using Google Analytics.
You can use these metrics to look at organic traffic and goals (or various eCommerce metrics) by landing page, which means you’re specifically looking at who’s converting among the people who come to the site from organic search (vs. who could have visited your site from search advertising, for example).
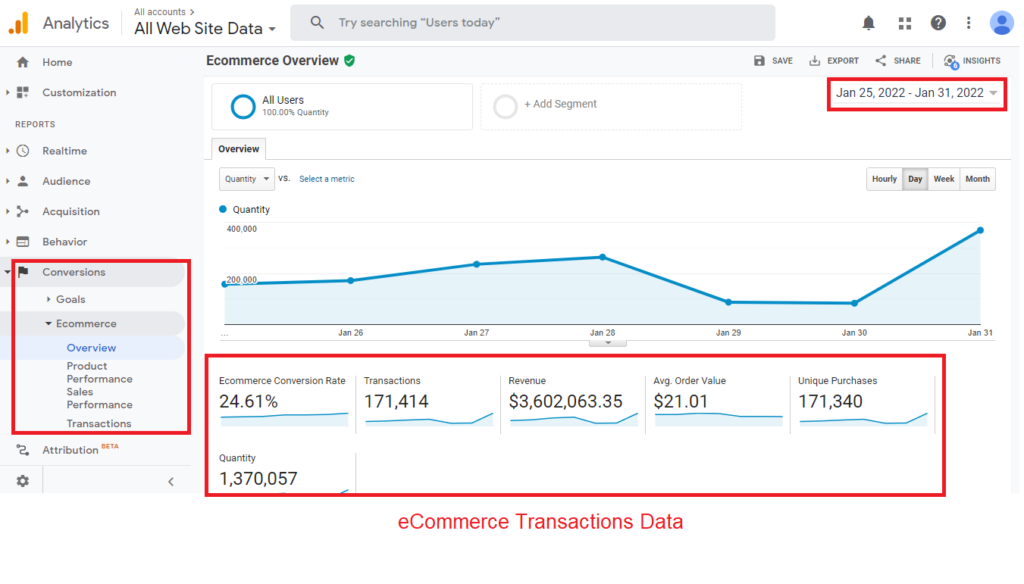
It seems pretty simple. And generally, for most businesses, this is a good way to measure the success of your SEO efforts at first.
But, again, there are a few caveats and nuances to keep in mind when using this data. Web analytics is not always perfect.
If you are moving your business from billboards or newspaper advertising to online marketing, you will likely be impressed with the volume and accuracy of the data available.
But sometimes there can be data tracking issues. Therefore, we advise you to treat this with some skepticism and from time to time correlate metrics data, for example, with your real income.
Useful Read: Practical Guide On How To Optimize Your eCommerce Site For More Sales
And a Few More SEO Considerations
For many companies, having a proper understanding of the technical aspects of SEO, tracking keywords, and having a link strategy in place is all there is to know about SEO. However, there are some specific cases and types of businesses that should be associated with certain types of searches.
Several types of search environments requiring unique approaches:
* International search engine optimization.
Different countries and languages have different approaches to site ranking. All of these approaches have their pros and cons.
* Local SEO.
For small companies and franchises, getting a local ranking in Google My Business is a very important ranking factor and almost the most valuable organic traffic available.
* Search Engine Optimization In The App Store And Google Play.
If you have an app that offers a company’s core product or allows mobile users to interact with a business, showing your app in search results, among others, can be very important. It’s also called App Store Optimization (ASO), SEO for apps listed on Google Play and Apple App Store.
So, what is next?
So, if you’ve come this far and read this long read, then you should already have an idea of how search engines rank sites, and how you can position your own website and business to generate more search traffic from search engines. What to do next?
Set your priorities. No website handles every aspect of search engine optimization flawlessly. Think about what you are good at. And if you have the budget and the resources, then combined, it will give your business the best return on investment.
If you’re good at creating and promoting content, then figure out which keywords to use and focus your efforts on those.
If you have a large and complex site, focus on proper technical SEO (or hire someone who can handle it).
If you are a small business that would benefit from ranking by very specific geographic criteria, but nothing more, focus your efforts on local SEO (and then maybe focus on other marketing tasks once you start to see the return on your efforts in this direction).
Always remember that the ultimate goal of any search engine optimization activity is to increase the reach and traffic of your business or website content. Look for ways that search engine traffic can help not only your website but also your business as a whole.
Leave a Reply